Mục lục
Understanding your variable costs is essential for small and mid-sized businesses. The higher your variable costs, the lower your profit margin, meaning your business makes less money. Different industries tend to have more fixed or variable costs, depending on the nature of the service or product they provide. To determine the total variable cost, simply multiply the cost per unit with the number of units produced. With a thorough understanding of variable costs, companies can set prices that cover these costs and also account for fixed costs, ensuring profitability. To determine total variable cost, simply multiply the cost per unit with the number of units produced.
Cost Per Unit

In other words, they fluctuate depending on the level of production or sales. As the volume of activity increases, variable costs increase; conversely, as the volume of activity decreases, variable costs decrease. For example, the chair company gets an order for 30 chairs for a total selling price of $2,400. To find variable cost per unit, we add the cost per unit in materials ($25) and direct labor costs ($25), and multiply it by our total quantity of output (how many chairs are produced for the order).
Example of Variable Costs
If companies ramp up production to meet demand, their variable costs will increase as well. If these costs increase at a rate that exceeds the profits generated from new units produced, it may not make sense to expand. A company in such a case will need to evaluate why it cannot achieve economies of scale. In economies of scale, variable costs as a percentage of overall cost per unit decrease as the scale of production ramps up. what is accounts receivable days formula and calculation doesn’t add fixed overhead costs into the price of a product so it can give a clearer picture of costs. These costs are hidden in inventory and don’t appear on the income statement when assigning these fixed costs to the cost of production, as absorption costing does.
Variable Cost: Definition, Formula, and Examples
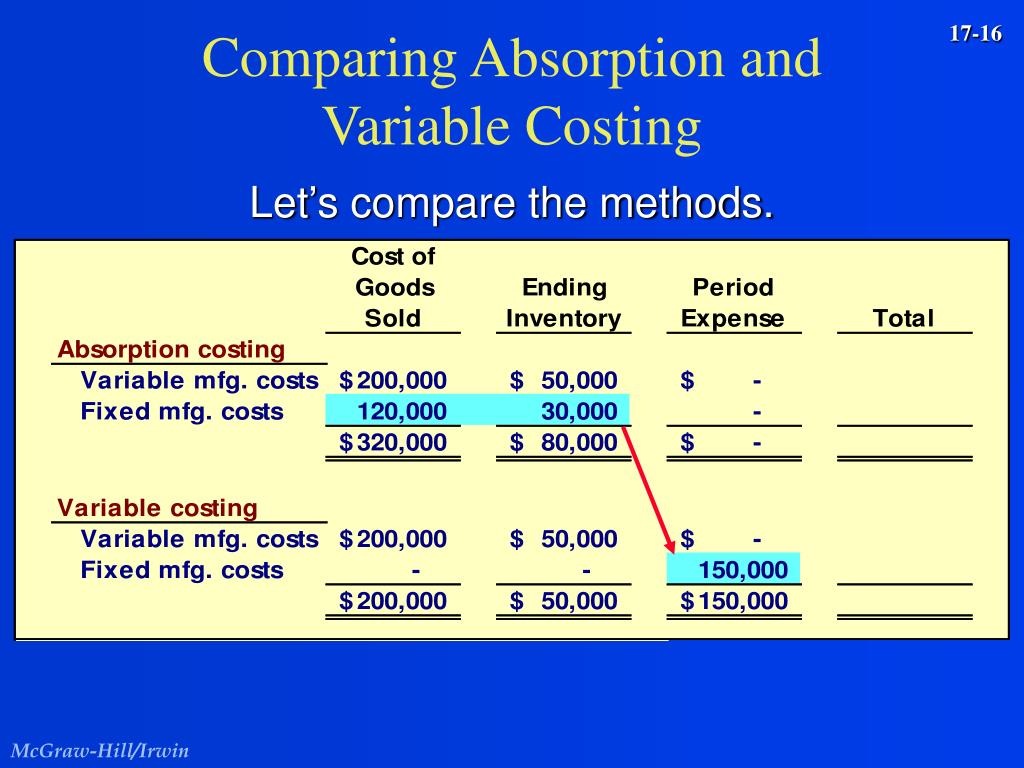
Under absorption costing, fixed factory overhead is allocated to the finished goods inventory account and is expensed to cost of goods sold when the product is sold. An example of a variable cost per unit would be if a company makes chairs. Each chair costs $25 in direct labor and $25 in direct materials to produce.
- Sales commissions, for example, are also considered variable because the size of a commission is tied to the volume of products sold by an employee.
- A variable cost is an expense that changes in proportion to how much a company produces or sells.
- Reduction in variable costs can result in a lower breakeven point, increasing the possibility of generating profit at lower sales volumes.
- For businesses, setting the right price for products or services is a balancing act.
- You should strive to keep variable cost per unit as low as possible since this will result in more profit per unit.
This calculation gives insight into the efficiency of the production process by assessing the variable cost per unit produced. A lower average variable cost indicates that the production process is more cost-efficient. Variable costs are expenses that vary in proportion to the volume of goods or services that a business produces.
Additional Resources
Therefore, a company can use average variable costing to analyze the most efficient point of manufacturing by calculating when to shut down production in the short term and even when to shut down a plant. In accordance with the accounting standards for external financial reporting, the cost of inventory must include all costs used to prepare the inventory for its intended use. It follows the underlying guidelines in accounting – the matching principle.
One of the most common uses for variable expense info is to set prices for your products or services. Material substitution, when done right, can be a strategic move to manage variable costs effectively. This might mean reducing idle time, optimizing the use of raw materials, or improving production workflows. One of the primary limitations of variable costs is the difficulty in predicting sudden shifts. By constantly evaluating and adjusting resource allocation based on variable cost data, businesses can ensure they’re operating efficiently and maximizing returns. Examples of fixed costs are employee wages, building costs, and insurance.
Understanding these factors can help businesses strategize better and maintain optimal operations. Let us understand why businesses use both absorption and variable costing calculator through the discussion below. The costs of production are always a factor that businesses want to perfect as this factor ultimately decides profitability and their overall growth in the market. Both variable and absorption are factors that are often misunderstood for one another. However, it is important to understand the differences between the two. For this reason, variable costs are a required item for companies trying to determine their break-even point.
If the differences between the two still seem unclear, you should get a better sense of them with the examples of fixed vs. variable expenses below. Essentially, if a cost varies depending on the volume of activity, it is a variable cost. For businesses, setting the right price for products or services is a balancing act.

